diode definition -ai
introduction to diode definition -ai
This article explores the definition of a diode, its types, applications, and its impact in AI-driven electronics. Whether you’re an electrical engineering student, an AI developer, or a tech enthusiast, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know about diodes in a structured and engaging way. diode definition -ai
What Is a Diode? A Clear Definition
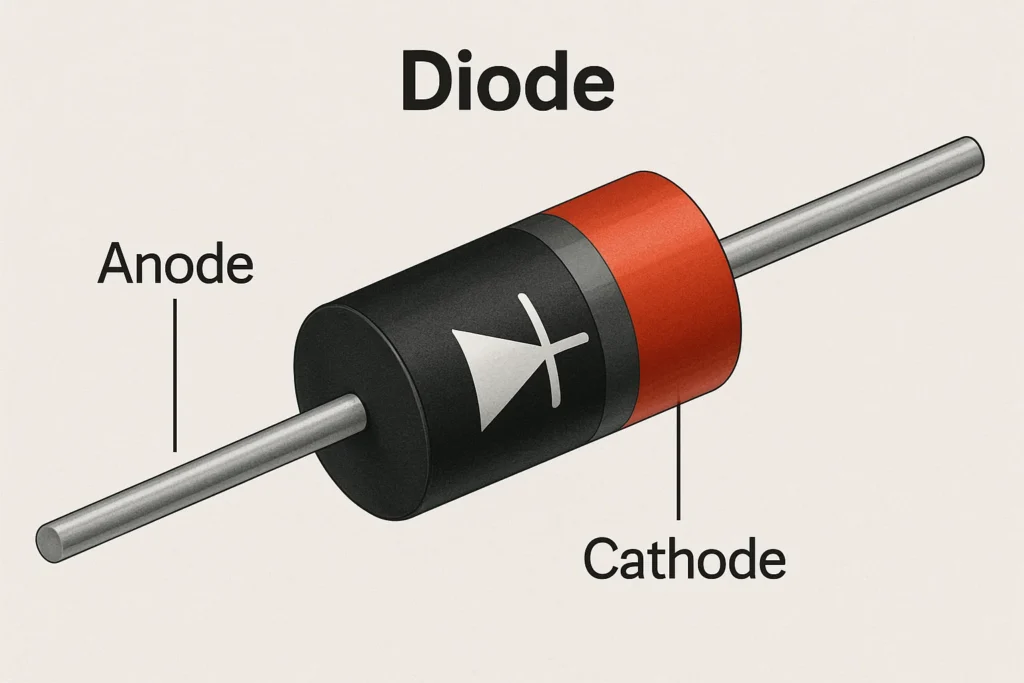
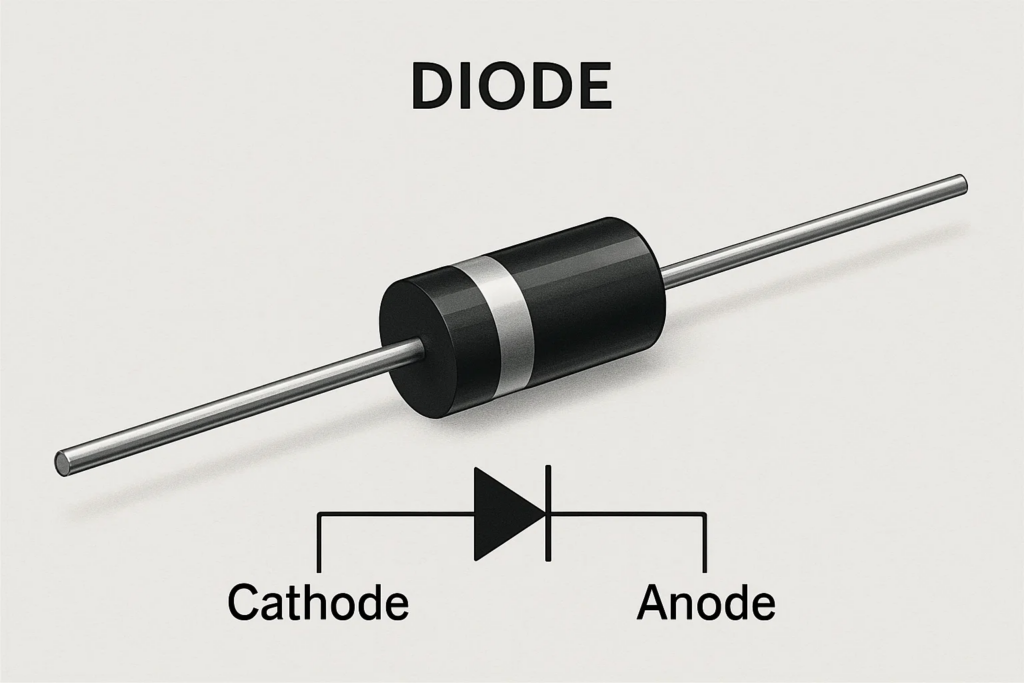
A diode is an electronic device that has two terminals and permits the flow of current in only one direction. Imagine a one-way valve for electricity. It is constructed by combining two semiconductor materials, P-type and N-type, to create a PN junction. This special feature makes the diode an indispensable part of both analog and digital circuits. diode definition -ai
Key Characteristics of Diodes
Unidirectional conduction: Easy flow of current in the forward direction but hard to pass in the reverse direction.
Low forward voltage drop: Usually on the order of 0.7V for silicon diodes and 0.3V for germanium. diode definition -ai
High reverse resistance: Stops unwanted flow of current when reverse-biased.
Fast switching speed: Required in modern digital circuits.
Simple Working Principle of a Diode
The magic of the diode is in its PN junction. When a diode is forward-biased (positive to P-side, negative to N-side), holes and electrons migrate towards the junction, enabling current to flow. When reverse-biased, the depletion region increases, preventing the current. diode definition -ai
This basic behavior is what makes diodes so useful in rectifiers, clippers, voltage regulators, and many other applications.
Types of Diodes and Uses
- Basic PN Junction Diode
Used in simple rectification and protection circuits. - Zener Diode
Permits current to pass in the reverse direction when the voltage is beyond a specified level—perfect for voltage regulation. diode definition -ai - Schottky Diode
Provides low forward voltage drop and high-speed switching, usually applied in RF and digital circuits. - Light Emitting Diode (LED)
Generates light when an electric current passes through it. Used in displays, indicators, and optical communications. diode definition -ai - Photodiode
Converts light into an electric current, extensively applied in sensors and light devices. - Tunnel Diode
Applied in microwave and high-frequency applications owing to its negative resistance characteristic. - Varactor Diode diode definition -ai
Serves as a variable capacitor, applied in RF design and tuning circuits.
Applications of Diodes in Everyday Electronics
Diodes are used in virtually every contemporary electronic device. Some examples include: diode definition -ai
Power Supplies: Rectifiers utilize diodes to convert AC to DC.
Signal Demodulation: Applied in AM radios to pull audio from carrier waves.
Voltage Clamping: Saves sensitive electronics from voltage spikes.
Logic Gates: Diodes find applications in simple digital logic circuits.
LED Lighting: LED diodes are ubiquitous in lighting arrangements today.
Diodes and Artificial Intelligence: How They Work Together
As we progress toward AI-enabled intelligent devices, the function of semiconductors—such as diodes—is more important than ever. diode definition -ai
- Diodes in AI Hardware Infrastructure
AI systems depend upon compute-intensive hardware, particularly GPUs, TPUs, and neural network processors. These consist of:
Power regulation circuits: Diodes help in smooth power supply.
Thermal control systems: Diodes assist with thermal sensors and cooling systems.
Signal routing and protection: High-speed diodes guard sensitive ICs in AI chips.
- Diodes in AI-Powered Devices
From smartphones to self-driving cars, AI-powered devices employ diodes for: diode definition -ai
Battery protection
Data transmission
Sensor integration
Motor control in robotics
- Photodiodes and Computer Vision
Photodiodes are part of vision systems, enabling AI algorithms to translate light signals. Uses include:
Facial recognition
Object detection
Automated inspection in manufacturing
Why Diodes Matter in AI-Centric Electronics
Reliability and Efficiency
AI systems need solid and stable components. Diodes provide quick response, voltage stability, and effective energy management, which are critical to AI functions based on real-time computing. diode definition -ai
Miniaturization and Integration
Newer AI devices are becoming smaller and more intelligent. Diodes enable miniaturized circuit designs, which provide high-density integration without sacrificing performance.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
AI computing workloads are power intensive. Diodes such as Schottky and Zener types help in effective power consumption, lowering thermal load and prolonging battery life in edge AI devices. diode definition -ai
Trends of the Future: Smart Diodes and AI Co-design
- Diodes in Neuromorphic Computing
Neuromorphic chips replicate the human brain. Scientists are investigating diode-resistor networks for simulating synaptic behavior, opening new horizons in brain-inspired AI. - AI in Diode Design and Simulation
Artificial intelligence tools are simulating, optimizing, and manufacturing diodes quicker and more precisely. Machine learning can even examine thermal performance, forecast lifetime, and detect manufacturing faults. - Flexible and Printed Diodes
With flexible electronics becoming popular, printed diodes are finding applications in wearable AI devices, IoT sensors, and flexible displays. diode definition -ai
Common Misconceptions About Diodes
- All Diodes Are the Same
Not true. Every variety has distinct electrical properties customized for various applications. diode definition -ai - Diodes Only Block Current
Wrong. Most diodes are active devices—like Zener, tunnel, and photodiodes—with dynamic characteristics. - LEDs Are Just Light Bulbs
No. LEDs are semiconductors that produce light by electroluminescence with rapid switching and low power requirements, ideal for AI visual signals. diode definition -ai
Troubleshooting Diodes in Electronic Circuits
Signs of a Faulty Diode
No current flow in either direction
Short circuit across terminals
Device overheating
Voltage drop too high or too low
Testing Tools
Multimeter: Apply diode test mode.
Oscilloscope: Observe switching behavior real-time.
Curve Tracer: Inspect voltage-current characteristic curve.
Selecting the Proper Diode for Your AI Application
When choosing a diode, take into consideration:
Current Rating: Should be able to sustain the load.
Reverse Voltage: Must support maximum reverse voltage in your system.
Switching Speed: Essential for high-frequency AI circuits.
Power Dissipation: Consider thermal management.
Example: In an edge AI camera module, a Schottky diode is perhaps best suited because of its fast switching speed and low forward voltage drop.
The Future of Diodes in AI and Advanced Electronics
Diodes are not just passive parts—they’re powering the next generation of electronics and AI innovations. As AI edge computing, wearable technology, and neuromorphic chips advance, so will the requirements for performance and complexity on diodes.
With graphene-based diodes, nano-scale tunnel junctions, and AI-driven design automation, we are entering an era where diodes are not just components—they’re catalysts of innovation. diode definition -ai
Conclusion
The humble diode has quietly powered technological revolutions for over a century. Today, as artificial intelligence pushes the boundaries of possibility, diodes remain central to delivering speed, reliability, and precision across devices and platforms. diode definition -ai
FOR MORE INFORMATIVE REVIEWS, VISIT: TECHBETIME | BUZZCRAZE | TRENDYINFO



